The Ultimate Guide to Asphalt Shingle Roofs
Asphalt shingle roofs are one of the most popular roofing options for homes due to their affordability, durability, and aesthetic appeal. This guide will take you through the history, types, pros and cons, lifespan, common problems, maintenance, manufacturing process, and additional aspects of asphalt shingle roofs.
History of Asphalt Shingle Roofs
When was shingle roof invented?
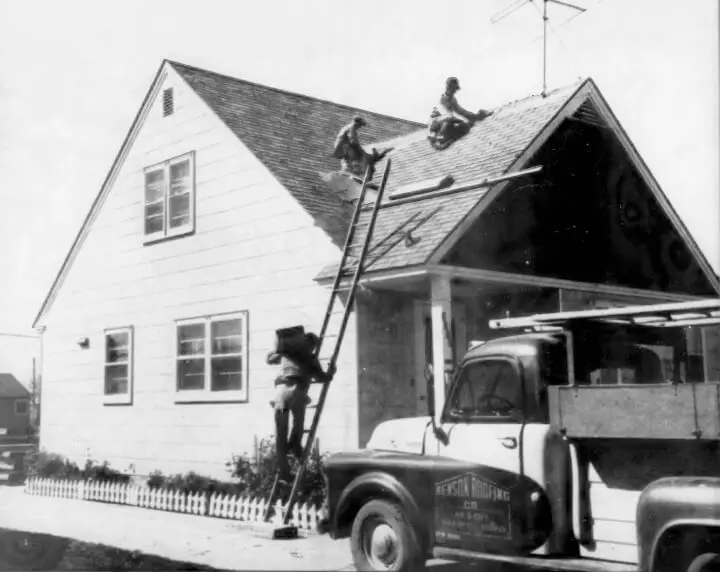
Asphalt shingles were introduced in the early 1900s.
Who Invented Asphalt Shingle?
Henry M. Reynolds from Grand Rapids, Michigan, is credited with inventing asphalt shingles.
How Did They Evolve?
Asphalt shingles started as roofing felt coated with asphalt. Granules were later added to improve durability and fire resistance. By the 1930s, asphalt shingles became widely popular in the United States.
Evolution of Asphalt Shingles
Over time, asphalt shingles evolved with advancements in materials and manufacturing processes. This included the transition from organic felt to fiberglass mat, improvements in asphalt saturation techniques, and developments in design styles such as architectural and luxury shingles.



https://archive.org/
History of Asphalt Shingle Roofs

https://archive.org

https://archive.org
When was shingle roof
invented?
Asphalt shingles were introduced in the early 1900s.
Who Invented Asphalt Shingle?
Henry M. Reynolds from Grand Rapids, Michigan, is credited with inventing asphalt shingles.

https://archive.org
How Did They Evolve?
Asphalt shingles started as roofing felt coated with asphalt. Granules were later added to improve durability and fire resistance. By the 1930s, asphalt shingles became widely popular in the United States.
Evolution of Asphalt Shingles
Over time, asphalt shingles evolved with advancements in materials and manufacturing processes. This included the transition from organic felt to fiberglass mat, improvements in asphalt saturation techniques, and developments in design styles such as architectural and luxury shingles.
Types of Asphalt Shingles

Three-Tab
Shingles
These shingles have three cutouts or tabs along their lower edge, giving them a flat, consistent appearance.

Pros
- Cost-Effective: Affordable and budget-friendly.
- Simplicity: Easy and quick to install.
- Uniform Look: Provides a simple, clean appearance.

Cons
- Durability: Less durable with a lifespan of 15-20 years.
- Wind Resistance: Lower wind resistance, rated up to 60 mph.
- Aesthetic Variety: Limited style and color options.

Architectural
(Dimensional) Shingles
These shingles have three cutouts or tabs along their lower edge, giving them a flat, consistent appearance.

Pros
- Durability: More robust with a lifespan of 20-30 years or more.
- Wind Resistance: Higher wind resistance, rated up to 110 mph or higher.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Wide variety of styles, colors, and textures.
- Increased Value: Enhanced appearance and longevity can increase

Cons
- Cost: More expensive than three-tab shingles.
- Weight: Heavier, may require additional roof support.

Luxury
(Designer) Shingles
These shingles have three cutouts or tabs along their lower edge, giving them a flat, consistent appearance.

Pros
- Aesthetic Appeal: High-end look.
- Durability: Long lifespan, up to 50 years or more.
- Performance: Excellent performance in various weather conditions.

Cons
- Cost: Most expensive type of asphalt shingle.
- Weight: Heavier and may require additional structural support.
- Installation: Due to their weight and premium features, luxury shingles require skilled installation by experienced professionals.
Pros and Cons of
Asphalt Shingle Roofs

Pros
- Affordable: Cost-effective compared to other roofing materials.
- Variety: Available in many colors and styles.
- Easy to Install: Quick and simple installation process.
- Durable: Good resistance to wind and weather when properly maintained.
- Fire Resistant: Most have good fire resistance ratings.
- Recyclable: Old shingles can be recycled into asphalt for roads.

Pros
- Lifespan: Shorter lifespan compared to materials like metal or slate.
- Maintenance: Regular inspections and maintenance are required.
- Environmental Impact: Manufacturing and disposal can affect the environment.
- Performance in Extreme Weather: Can be damaged by severe weather.

Lifespan of
Asphalt Shingles
Factors Affecting Lifespan: Installation quality, climate, roof angle, and regular maintenance can significantly impact the lifespan of asphalt shingles.
Three-Tab Shingles
Lifespan of 15-20 years
Architectural Shingles
Lifespan of 20-30 years or more
Luxury Shingles
Lifespan of up to 50 years or more
Lifespan of
Asphalt Shingles
Three-Tab Shingles
Lifespan of 15-20 years
Architectural Shingles
Lifespan of 20-30 years or more
Luxury Shingles
Lifespan of up to 50 years or more
Factors Affecting Lifespan: Installation quality, climate, roof angle, and regular maintenance can significantly impact the lifespan of asphalt shingles.
Common Problems and Damages
Shingle Hail Damage
WHAT IS IT?
Dents or pockmarks caused by hailstones.
IDENTIFICATION:
Look for scattered dents and soft spots. Press on shingles to check for softness.
SOLUTION:
Replace damaged shingles or the entire roof if damage is extensive.
Shingle Curling
WHAT IS IT?
Edges or corners of shingles turn up or down.
CAUSES:
Poor ventilation, improper installation, or old age.
IDENTIFICATION:
Raised edges or corners.
SOLUTION:
Improve ventilation, ensure proper installation, and replace affected shingles.
Shingle Staining
WHAT IS IT?
Dark streaks or discoloration caused by algae, mold, or mildew.
CAUSES:
Humid climates, lack of sunlight, organic debris accumulation.
IDENTIFICATION:
Black or dark streaks.
SOLUTION:
Clean with water and bleach mixture. Install zinc or copper strips to prevent future growth.
Shingle Blisters
WHAT IS IT?
Raised areas caused by trapped moisture or air.
CAUSES:
Poor ventilation, manufacturing defects.
IDENTIFICATION:
Raised bumps that feel soft and can pop.
SOLUTION:
Replace affected shingles and improve ventilation.
Shingle Alligatoring
WHAT IS IT?
A pattern of cracks resembling alligator skin.
CAUSES:
UV exposure, old age, or using the wrong materials.
IDENTIFICATION:
Series of cracks forming a pattern.
SOLUTION:
Replace affected shingles with better UV protection.
Shingle Delamination
WHAT IS IT?
Layers of shingles separate, causing the top layer to peel away.
CAUSES:
Manufacturing defects or severe weather.
IDENTIFICATION:
Peeling or separating layers.
SOLUTION:
Replace delaminated shingles.
Shingle Granule Loss
WHAT IS IT?
Granules wear away from the shingle surface.
CAUSES:
Aging, severe weather, improper installation.
IDENTIFICATION:
Bare spots on shingles, granules in gutters.
SOLUTION:
Replace shingles if granule loss is extensive.
Shingle Nail Pops
WHAT IS IT?
Nails push up through shingles, creating raised bumps.
CAUSES:
Improper nailing, thermal expansion, or contraction of the roof deck.
IDENTIFICATION:
Nails protruding through shingles.
SOLUTION:
Hammer down nails and seal with roofing cement. Replace damaged shingles.
Shingle Mechanical Damage
WHAT IS IT?
Physical damage from foot traffic, falling branches, or other impacts.
IDENTIFICATION:
Visible signs of impact or scuff marks.
SOLUTION:
Replace damaged shingles and avoid walking on the roof.
Shingle Blistering
WHAT IS IT?
Small raised areas caused by trapped moisture or gas.
CAUSES:
Poor ventilation or manufacturing defects.
IDENTIFICATION:
Bubble-like protrusions that can pop.
SOLUTION:
Ensure proper ventilation and replace affected shingles.
Creases Shingle by Wind Damage
WHAT IS IT?
Shingles lift and crease when they settle back down.
IDENTIFICATION:
Horizontal or diagonal fold lines.
SOLUTION:
Replace creased shingles and ensure they are properly secured.
Shingle Brittleness
WHAT IS IT?
Shingles become brittle and prone to cracking.
CAUSES:
Aging, UV exposure, extreme temperature changes.
IDENTIFICATION:
Shingles crack easily when bent.
SOLUTION:
Replace brittle shingles and use shingles with better UV and temperature resistance.
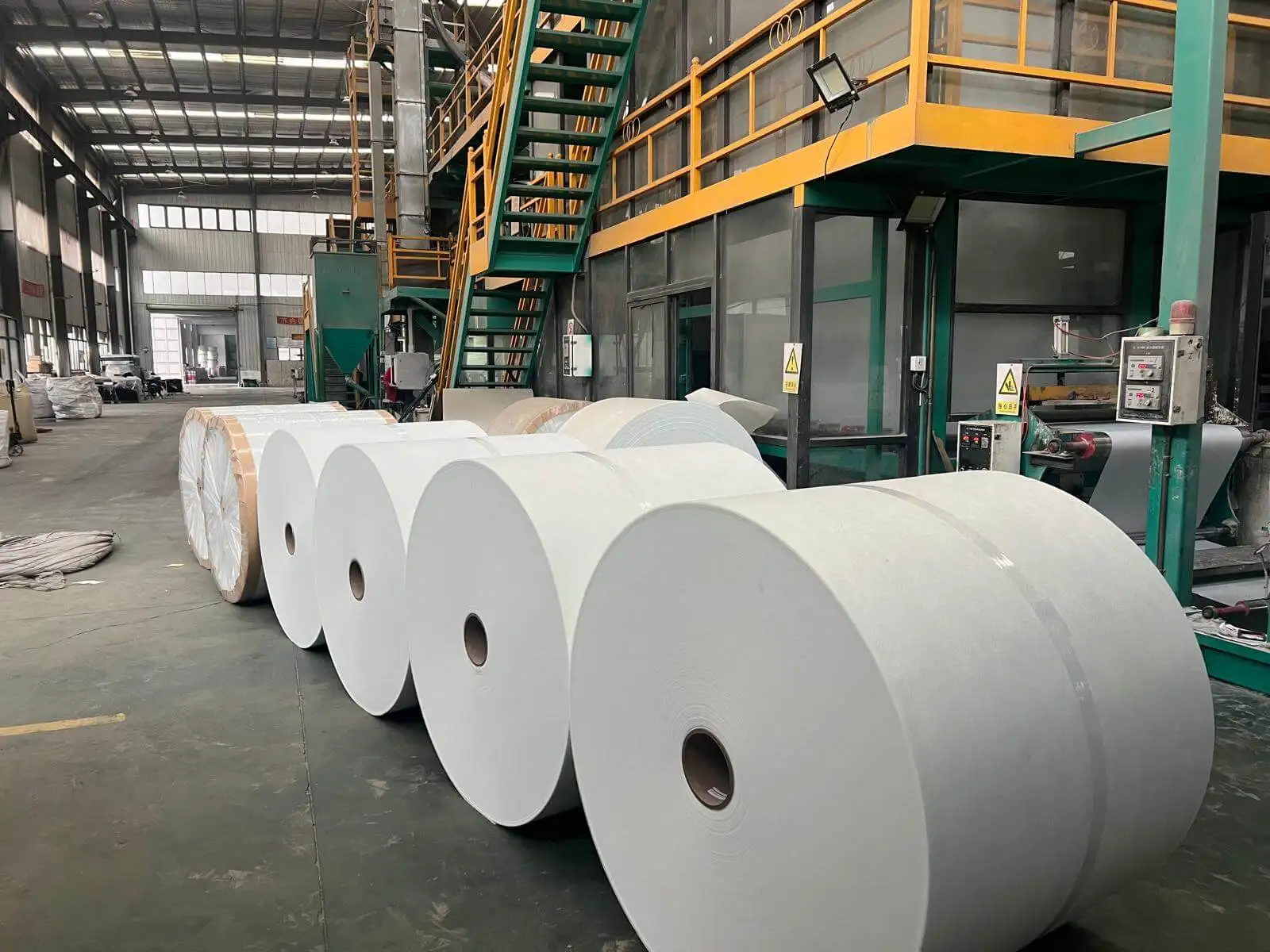

How Asphalt Shingles are Manufactured
Creating the Base Material:

- Organic Felt: Made from recycled paper or wood fibers, saturated with asphalt.
- Fiberglass Mat: Made from thin glass strands bonded with resin, stronger and more fire-resistant than organic felt.
Saturating with Asphalt:

- Asphalt Saturation: The base material is saturated with hot asphalt to make it waterproof and durable.
- Coating with Asphalt: Additional asphalt is applied on both sides of the base material.
Adding Granules:

- Granule Application: While the asphalt is still hot, mineral granules are embedded on the top surface to protect from UV rays and weather, and to add color.
Cooling:

- Cooling Process: The asphalt-coated mat with granules is cooled to solidify the asphalt and ensure the granules adhere properly.
Cutting and Shaping:

- Shingle Cutting: The continuous sheet is cut into individual shingles. For three-tab shingles, this includes creating three uniform cutouts or tabs.
Packaging and Distribution:

- Quality Control: Shingles undergo quality checks to ensure they meet standards.
- Packaging: Finished shingles are bundled and packaged for distribution.
- Distribution: Shingles are shipped to distributors, retailers, and contractors.
Environmental Impact of
Asphalt Shingle Roofs
Recyclability
Asphalt shingles can be recycled into
asphalt for roads, reducing waste.
Energy Efficiency
Reflective shingles can reduce cooling
costs by reflecting solar heat.

Sustainability
Some manufacturers offer eco-friendly
shingles made from recycled materials.
Stay Tuned!
Roof Ventilation
Importance: Proper ventilation helps prevent moisture buildup, extend roof lifespan, and improve energy efficiency.
Types: Ridge vents, soffit vents, gable vents, and roof turbines are common ventilation options.
Energy Efficiency
Cool Roof Shingles: Reflective shingles can reduce heat absorption and lower cooling costs.
Insulation: Proper attic insulation complements energy-efficient roofing.
Roof Replacement
Signs for Replacement: Age, extensive damage, leaks, and structural issues may necessitate roof replacement.
Tear-Off and Disposal: Old shingles are removed and disposed of properly before new installation.
Fire Resistance
Fire Ratings: Asphalt shingles have varying fire resistance ratings (Class A, B, or C), with Class A being the most fire-resistant.
Roof Maintenance
Regular Inspections: Check for damage, leaks, and signs of wear regularly.
Gutter Cleaning: Keep gutters clean to prevent water backup and damage.
Debris Removal: Remove debris such as leaves and branches from the roof.
Local Regulations
and Codes
Permits: Check local regulations for necessary permits before roofing projects.
Building Codes: Ensure roofing materials and installations comply with local building codes.

For a free consultation and to discuss the best options to re-roof a house in Florida, please call us or schedule your free roof inspection by clicking the button below.